CHAPTER: 9 PEDAGOGICAL ANALYSIS BASED ON UNIT ALALYSIS
CHAPTER: 9
Pedagogical Analysis Based on
Unit Analysis
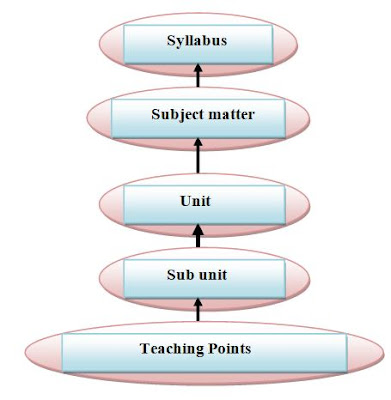
A good syllabus is that in which contents items are
divided onto different units which are further divided into sub units. It makes
the teaching learning process easy and it also helps the teacher and the
learners to feel more convenient from the teaching learning point of view. The
approach of unit wise teaching, unit wise learning, and unit wise testing is
called as unit approach. According to NCERT, “A unit of study may understand as
a block of closely related subject matter which can conveniently be over viewed
by the learners within a short span of time. The size of a unit could, of
course, vary.”
(I)
Unit and its analysis: For making the teaching more effective and interesting a good teacher
has to divide the full syllabus into some units as per his/her convenience. In
a unit there is a interrelated subject matter. Here unit means to cover topic
from syllabus and analysis means bifurcating a unit into sub units.
(II) Selection of objectives for the unit: For effective unit analysis it is expected that a teacher
has to formulate unit wise instructional objectives in behavioural terms. The
knowledge of subject matter helps the teacher in formulating instructional
objectives. In unit analysis, not only the scholastic objectives but also the
non-scholastic objectives should be fixed up.
Scholastic
Objectives
Ø
Knowledge: (i) The
students should have to know the differences between active and passive voice.
(ii) They are able
to recall and recognize how conversation of different types of sentences from
active to passive and vice versa.
Ø
Understanding: (i)
The students should have to understand the different rules for changing all
type of sentences from active voice into passive voice. (ii) They have good
understanding and they can clarify before others all about the rules and
regulations of active and passive voice.
Ø
Skills: The
learners are able to develop all the skills of Reading, Writing, Listening and
Speaking.
Ø
Application: The
students are able to apply the knowledge of active and passive voice in their
real life situation in written and spoken.
Non Scholastic Objectives:
Ø Personality development
Ø Physical development
Ø Social development.
Ø Emotional development
(I)
Learning Experiences
Methods and Materials-: A variety of learning experiences will be provided to
the students to make teaching effective and interesting. Materials will be
presented by using activity method, group work etc. Teaching should be done
first to the whole class, then by dividing the whole class into two or more
groups. As per example when a teacher is going to teach about active and
passive voice, first the teacher help to the whole class to know when to use
the active and passive voice and the teacher also helps the students to know
the following rules and regulations of Active and Passive Voice. The passive
voice is formed with the suitable tense of the verb be followed by the past
participle.
Then the teacher may divide the whole
class into two groups. One student from first group will speak a sentence in
Active Voice. After that, one student from other group will stand and speak the
passive voice of that sentence. This type of practice will be carried on by
taking up one type of sentence at a time. In such case, there is need of
maximum participation of the students. The subject matter should be taken up
tense wise.
Examples
of matter are given below-:
The learning
experiences will be varying from subject to subject. So the English teacher has
to plan according to his subject and available resources and prepare a outline
of his teaching activity beforehand. For creating appropriate learning
situation and for providing good learning experiences to the students, the
teacher has to develop a sequence of teaching activity and prepare his lesson
plan beforehand. The teaching objective will be achieved when the teacher able
to provide appropriate learning experiences to the students. John Dewey
advocated that a major task of the teacher is to generated learning situation,
which will motivate to the students for performing certain activities. A
teacher role is to organize and control all the teaching activities. All the
learning experiences cannot be called as learning experiences. The following
are the main aspects of learning experiences-:
·
Teaching objectives
related to the topic.
·
Outline of the
courses.
·
Teaching methods and
techniques.
·
Maxims of teaching
and aids of teaching.
·
Text books and home
work.
·
Role of the teacher.
·
Relationship of the
teacher with the students.
·
Effective
communication skill.
·
Pedagogical
knowledge of the teacher.
(II)
Evaluation
Evaluation plays a vital role in the process of teaching
and learning. Evaluation is a continuous assessment of an individual. The
concept of evaluation can be applied with the help of unit plan and yearly
plan. Here all round development of an individual i.e scholastic and
non-scholastic achievement is taken into account. The teacher should held
weekly or bi-weekly test. The same proportion is to be maintained by testing
situation in terms of number of items. Three type-: Essay type, Objective type
and short answer type items are included in the test. The higher objectives can
be tested with the help of essay type of items. There should be coordination
between teaching and testing with the help of teaching objectives. The test
used in evaluation approach should be reliable and valid.
(III)
Steps involved in the preparation and utilization of a
Unit test
·
Preparation of the
questions according to the specified objectives and areas of the content.
·
Developing a blue
print regarding the form of the questions and the marks carried by each
questions.
·
Framing of
questions.
·
Assembling and
editing the questions.
·
Preparing a scoring
key for objective type items and marking scheme for short answer and essay type
items.
·
Question-wise
analysis should be undertaking.
…






Comments
Post a Comment